In today’s digital world, computer networks are the engine that keeps millions of devices connected around the globe. However, when we talk about networks, we often encounter two fundamental terms: LAN (Local Area Network) and WAN (Wide Area Network). Although both types of networks share the common goal of connecting devices, there are key differences that make them suitable for different scenarios. If you’ve ever wondered what these networks are and how they affect your daily interactions with technology, this article will offer a detailed explanation.
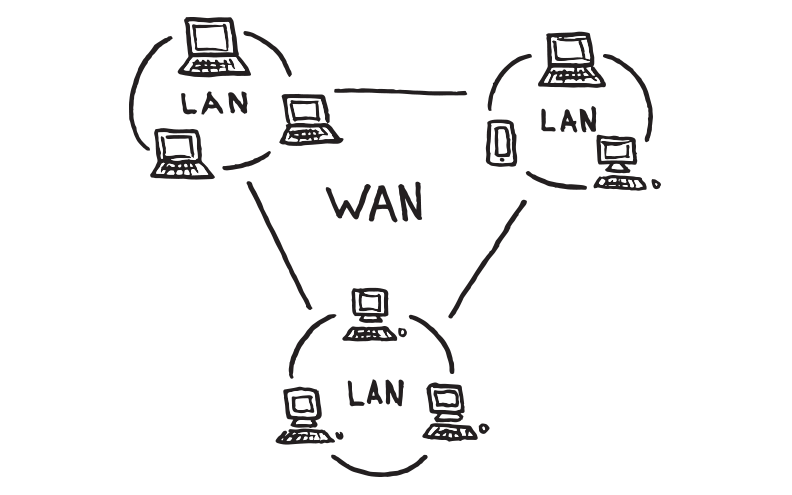
What is a LAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that covers a small geographical area, typically a home, office, or building. The purpose of a LAN is to interconnect devices such as computers, printers, servers, and other equipment within that limited area to share resources like files, applications, and Internet access. In a LAN, devices are connected via cables (Ethernet) or wirelessly (Wi-Fi), enabling fast and efficient communication.
Key Features of a LAN:
- Limited Range: Typically covers no more than a few blocks or a single building.
- Fast Speeds: Due to the proximity of devices, LANs typically offer high data transfer speeds, which facilitates the use of applications and services that require high performance.
- Low Implementation Cost: Setting up a LAN is relatively inexpensive compared to a WAN, as it requires less infrastructure and is easier to manage.
- Controlled Security: Security in a LAN is easier to manage because devices are within a controlled area. However, Wi-Fi networks can be vulnerable to intruders if not properly configured.
One of the reasons LANs are so popular is their ability to efficiently connect devices in a small space. Simply put, if you’ve ever connected your computer to a printer or shared files with family members in the same house, you’ve likely been using a LAN.
What is a WAN?
On the other hand, a Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers much larger geographical areas. Unlike a LAN, which is limited to a small environment, WANs can span cities, countries, or even entire continents. The primary feature of a WAN is that it connects multiple LANs across long distances. WANs often use technologies like telephone lines, submarine cables, satellites, and fiber-optic connections to transmit data.
Key Features of a WAN:
- Global Range: Can cover much larger geographical areas, such as cities, countries, or continents.
- High Costs: Implementing and maintaining a WAN requires more robust and expensive infrastructure, especially if it involves satellite links or high-speed dedicated connections.
- Variable Speeds: Although some modern WANs can offer fast speeds, connections in a WAN are generally slower than in a LAN due to the longer distances and the larger number of devices involved.
- Greater Management Complexity: Due to its size and the diversity of connections it involves, a WAN is harder to manage and secure than a LAN. WANs require more complex network infrastructure and must be constantly monitored.
WANs are essential for large organizations’ connectivity, as they allow communication between company branches or access to cloud services. In fact, when you access an online service like email or social media, you are likely using a WAN to connect to servers located in different parts of the world.
Main Differences Between LAN and WAN
Although LANs and WANs are both types of networks, their differences are significant and go beyond just geographical reach. Below are some of the main differences between them:
- Geographical Range
The most obvious difference between a LAN and a WAN is the geographical reach. LANs are designed to connect devices within a small, limited area, while WANs connect devices across large distances. In fact, WANs make it possible to connect different LANs. - Connection Speeds
In terms of speed, LANs are usually much faster than WANs. This is because LANs are limited to a small geographical area, which allows for more efficient and faster communication between connected devices. WANs, on the other hand, can be slower due to the long distances data must travel. - Implementation Cost
Setting up a LAN is generally cheaper than implementing a WAN. LANs require less infrastructure as they only connect devices within a small area, while WANs require much more complex and expensive communication infrastructure. - Security
LANs are generally easier to secure because of their limited size, making it easier to control access to the network. In contrast, WANs are more vulnerable due to their size and the multiple access points involved. However, both networks can benefit from advanced security measures such as firewalls, VPNs, and encryption.
LANs, like WANs, are crucial for the functioning of our digital networks. While LANs are ideal for connecting devices in local areas, WANs are essential for connecting these local networks globally. Although LANs are faster and easier to implement, WANs enable organizations and individuals to connect over long distances. Each network type has its advantages and limitations, and the choice between a LAN and a WAN will depend on the specific needs of the user or business.
In the following sections of this article, we’ll explore practical use cases, the technologies driving these networks, and how to choose the right network based on your needs. Keep reading to learn more about how LANs and WANs impact the modern world!
This analysis of the technologies behind LAN and WAN networks has shown how each type of network meets specific needs and plays a fundamental role in modern connectivity. In the next part of this article, we’ll explore how you can choose the right network based on your personal or business needs. Keep reading!
How to Choose the Right Network: LAN vs. WAN
Choosing between a LAN or a WAN largely depends on your specific needs, whether personal or business-related. To make an informed decision, it is essential to understand how each type of network fits different scenarios, considering factors like range, speed, cost, and security. Below, we’ll go over the key factors to consider when choosing between a LAN and a WAN.
- Range and Coverage
The first factor to consider is the area you want your network to cover. If you only need to connect devices within an office, home, or building, then a LAN will be the most suitable option. This type of network is ideal for situations where devices are relatively close, such as in a small business, school, or smart home.
On the other hand, if your goal is to connect multiple branches or offices in different cities, countries, or continents, then a WAN is the ideal choice. WANs are essential for multinational companies or any organization that needs to connect geographically distributed local area networks.
- Speed and Performance
Speed is a key aspect when choosing between a LAN and a WAN. If fast data transfer is crucial for your network, as in an environment with large amounts of data that need to be shared quickly, a LAN will be much more efficient. LANs, especially those using Ethernet cable connections or advanced fiber-optic connections, can offer speeds of up to 100 Gbps, making them ideal for tasks such as video editing, managing large databases, or using high-demand applications.
WANs, on the other hand, may experience some speed limitations due to the long distances data must travel and the more complex infrastructure. While advanced WANs can be fast, such as those using fiber-optic connections, they typically do not reach the speeds of LANs due to factors like latency and network congestion.
- Implementation and Maintenance Cost
The cost of setting up a network is one of the most important factors when deciding between a LAN or a WAN. LANs are more affordable because they require less infrastructure and equipment. You can set up a simple LAN with Ethernet cables, a switch, and a basic router, resulting in low upfront costs. Additionally, maintenance is relatively simple and inexpensive as it doesn’t involve long distances or complex equipment.
In contrast, WANs can be costly both in terms of initial implementation and ongoing maintenance. Installing fiber-optic links or satellite connections requires significant investment, and WANs require specialized equipment and staff to manage them. Furthermore, if you’re using an internet service provider to connect multiple locations, the costs of dedicated links and supporting infrastructure can quickly add up.
- Security
Security is one of the primary concerns when choosing a network, as cybersecurity threats are constantly increasing. LANs offer much more granular control over security because connected devices are within a geographically defined area, making it easier to implement protective measures like firewalls and monitoring systems. Additionally, wired connections are generally more secure than wireless connections, reducing the risk of intrusion.
In contrast, WANs require more complex security measures due to their size and the variety of connections involved. As data travels long distances and passes through public networks like the Internet, it’s crucial to implement strong security protocols such as VPNs, data encryption, and multifactor authentication to protect sensitive information. WAN security is harder to manage due to distributed access points, but with the right strategy, these networks can be as secure as LANs.
- Scalability and Flexibility
If you plan to expand your network in the future, either by adding more devices or covering a larger geographical area, network scalability will be an important factor to consider. LANs are easy to expand, as you only need to add more cables, switches, or routers to connect more devices. However, scalability has a limit since its reach is restricted to a local area.
On the other hand, WANs are designed to be highly scalable and can easily adapt as your organization’s needs grow. If you need to connect new branches or incorporate new technologies, WANs can expand to include more connections and services. However, expanding a WAN can be costly and may require significant investments in infrastructure, equipment, and telecommunications services.
- Business and Personal Use
- Business Use: LANs are essential for the internal operations of small and medium-sized businesses. They allow collaboration among teams within an office and resource sharing. In contrast, WANs are necessary for large businesses with offices in different locations or for businesses that need access to cloud services or remote data centers.
- Personal Use: For individual users, LANs are the more common option as they allow devices to connect at home for sharing resources like printers, file storage, and Internet access. WANs, on the other hand, are mainly used by internet service providers, large corporations, and users needing access to data or services outside their local environment.
Which Is the Best Option for You?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to whether a LAN or WAN is better; the choice depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you only need to connect devices in a limited space and want a cost-effective, high-performance solution, a LAN will be the ideal choice. LANs are perfect for homes, small offices, and local organizations that don’t require extensive geographical coverage.
However, if your goal is to connect multiple locations on a large scale, share resources globally, or access cloud applications, a WAN is essential. WANs are vital for multinational companies and organizations that need to ensure connectivity between geographically distributed branches or maintain access to remote services.
The key is understanding your connectivity needs and the characteristics of your environment. If you choose a WAN, make sure you have the resources necessary to manage its complexity and costs, and if you choose a LAN, enjoy the speed and simplicity of a more accessible and economical network.
Emerging Technologies in LAN and WAN Networks
As the digital world continues to evolve, both LAN and WAN networks are adopting new technologies that enhance their performance, efficiency, and adaptability. These innovations not only make networks faster and more secure but also open up new possibilities for businesses and individual users. In this section, we will explore some of the most relevant emerging technologies in LAN and WAN networks.
- Software-Defined Networks (SDN)
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is revolutionizing both LANs and WANs. SDN is a network architecture that separates the control plane (the network’s decision-making logic) from the data plane (the actual traffic flowing through the network). This allows for greater flexibility and control over networks, as administrators can manage the network in a centralized, programmable way without having to modify each individual device.
Benefits of SDN in LAN and WAN:
- Agility and Flexibility: With SDN, networks can quickly adapt to changes in demand, such as increased data traffic or the need for greater security. Administrators can implement network policies, such as bandwidth control, centrally without needing to reconfigure each device manually.
- Cost Optimization: SDN allows the use of standard, non-specialized hardware, reducing infrastructure costs for both LANs and WANs. Additionally, centralized management makes maintenance and updates easier.
- Better Control and Security: SDN allows for more effective security policies, segmenting traffic and better protecting the network from external or internal threats.
- 5G for WANs
The rollout of 5G is transforming the WAN landscape. While 4G networks already offer fast connections for mobile devices, 5G takes it further by providing much higher data transmission speeds, lower latency, and a much higher capacity for connecting multiple devices simultaneously.
Benefits of 5G for WAN:
- Ultrafast Speeds: 5G can offer speeds up to 10 Gbps, greatly improving the user experience, especially for bandwidth-heavy applications like HD video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing.
- Low Latency: 5G latency is much lower than previous networks, making it ideal for real-time applications like industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, and IoT networks.
- Massive Connectivity: 5G can connect millions of devices per square kilometer, which is crucial for smart cities and the Internet of Things.
The 5G revolution will enable businesses to create more agile and efficient WANs, improving global connectivity and reducing reliance on traditional cable or fiber-optic connections.
- Advanced Fiber-Optic Connections
Fiber-optic technology continues to be one of the most crucial technologies for high-speed WANs, but with the increasing demand for greater bandwidth, new techniques like ultra-high-capacity fiber-optics have emerged.
Benefits of Advanced Fiber Optics in WAN:
- High Bandwidth: Advanced fiber optics can support extremely high data transmission speeds, making them the preferred option for high-capacity WANs, such as those used by Internet service providers (ISPs) or large corporations.
- Long Distances with Minimal Signal Loss: Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber-optic cables can transmit data over long distances without significant signal degradation, making them ideal for networks that connect multiple geographical locations.
- Scalability: Fiber-optic networks offer exceptional scalability. As bandwidth demands grow, fiber-optic networks can adapt to provide higher speeds without needing an entirely new infrastructure.
- Mesh Wireless Networks for LANs
Mesh networks are gaining popularity in the LAN domain due to their ability to cover larger areas and provide more reliable connectivity. Unlike traditional Wi-Fi networks, where all devices connect to a single access point, mesh networks use multiple access points distributed to create a unified and broader network.
Benefits of Mesh Networks in LAN:
- Extended Coverage: Mesh networks can cover larger areas without losing signal strength. They are ideal for large homes, offices, or environments where thick walls can interfere with standard Wi-Fi signals.
- Redundancy and Reliability: In a mesh network, if one access point fails, other access points automatically take over, ensuring continuous connectivity without interruptions.
- Easy Expansion: Adding more devices to a mesh network is simple. You only need to add more access points, making the network easily scalable as needs grow.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is another emerging technology impacting both LANs and WANs. NFV enables the virtualization of network services like firewalls, load balancers, and gateways, using software instead of specialized physical hardware.
Benefits of NFV:
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating the need for costly physical equipment, NFV significantly reduces network infrastructure costs.
- Increased Flexibility: NFV allows network administrators to deploy and manage network services more flexibly, adapting to new demands or infrastructure changes.
- Better Scalability: With NFV, new network functions can be added without the need for more hardware, making it easier to expand the network as organizational needs grow.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Network Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is beginning to play a crucial role in managing both LAN and WAN networks. AI-powered solutions can analyze large amounts of data to predict and resolve network issues, improve performance, and automate management tasks.
Benefits of AI in Networks:
- Proactive Monitoring: AI tools can monitor networks in real-time and predict potential failures before they happen, allowing for early intervention and reducing downtime.
- Performance Optimization: AI can dynamically optimize bandwidth usage, ensuring that critical applications receive the priority they need and improving overall network efficiency.
- Task Automation: AI also allows for the automation of repetitive tasks, such as device configuration, IP address assignment, and network change management.
As these emerging technologies continue to evolve, LANs and WANs are becoming faster, more secure, flexible, and scalable. If you are looking to improve your network or update your infrastructure, it’s essential to stay informed about these innovations to fully leverage their potential.
In the next section of this article, we’ll discuss how the future of networks is likely to be influenced by the convergence of technologies and what this means for users and businesses in terms of global and local connectivity. Keep reading to discover more!
The Future of Networks: Technology Convergence and Its Impact on LAN and WAN
As technologies advance and user and business needs change, both Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) are undergoing a radical transformation. The convergence of emerging technologies is shaping smarter, more agile, and efficient networks that integrate different solutions, such as virtualization, 5G, AI, and software-defined networks (SDN). In this section, we will explore how this convergence is impacting LAN and WAN networks and what it means for the future of connectivity.
- Convergence of LAN and WAN Networks
The distinction between LAN and WAN may become less pronounced in the near future. With the deployment of technologies like SDN, NFV (Network Function Virtualization), and 5G, the boundaries between local and wide area networks are starting to blur. Instead of relying on separate physical infrastructures for LANs and WANs, businesses may operate more integrated and flexible networks that can adapt to changing demands without the need to create entirely separate networks.
Example of Convergence: Hybrid 5G Networks
5G networks not only enhance WAN connections but also have the potential to integrate with local LANs. This hybrid approach, where a high-capacity LAN connects through a 5G WAN, will enable businesses to access resources more efficiently and with greater flexibility. Additionally, the integration of SDN and NFV in these networks could simplify management, as both local and wide area networks could be controlled from a centralized platform.
- Automation and Autonomous Networks
One of the biggest trends in the evolution of LAN and WAN networks is automation. AI and SDN technologies are enabling autonomous networks that can self-regulate, adapt to data traffic needs, and resolve issues without human intervention.
Benefits of Autonomous Networks:
- Simplified Management: Network administrators will no longer need to make constant manual adjustments. Smart networks can adapt to new traffic demands, identify bottlenecks, and reroute traffic efficiently.
- Reduced Human Error: Automation significantly reduces human errors when managing configuration, updates, and network security.
- Enhanced Resilience: In the event of a network component failure, an autonomous network can redirect traffic, reconfigure network topology, and quickly restore connectivity.
In the future, LAN and WAN networks could operate more autonomously, with AI making real-time decisions to optimize connectivity and performance.
- Software-Defined Networks (SDN) and Their Role in Convergence
SDN is not only revolutionizing LANs and WANs but also enabling both types of networks to be managed in a centralized, flexible manner. Traditionally, LANs and WANs were managed separately with different administration systems and configurations. However, SDN allows for a single control plane that can manage both local and wide area infrastructures.
How SDN Facilitates Convergence:
- Unified Management: With SDN, network administrators can manage both local and wide area connections from a single platform. This simplifies monitoring, control, and optimization, leading to more efficient and cost-effective network management.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SDN enables networks to scale according to needs, adding new resources and capabilities as required. This is especially important for hybrid networks combining LAN and WAN.
- Agility: Software-defined networks allow greater agility, as changes and adjustments can be implemented quickly without the need to reconfigure physical devices, making them ideal for companies operating in dynamic environments.
- The 5G Revolution and Its Impact on Global Connectivity
5G is reshaping how we perceive WANs, but its impact also extends to LANs, especially in terms of high-capacity wireless connectivity. As 5G is deployed globally, it will enable WANs to reach new data transmission speeds and lower latencies, which will, in turn, enhance the overall performance of connected LANs.
How 5G Affects LAN and WAN:
- Higher Speeds and Lower Latency: 5G connectivity offers speeds up to 10 Gbps and latencies as low as 1 ms, significantly enhancing user experience for high-quality video conferencing, online gaming, and cloud-based services.
- Convergence of Telecommunications Networks and Local LANs: 5G networks will allow LANs to connect to high-speed WANs, using technologies like edge computing to process data closer to where it is generated, reducing the need to transfer large amounts of information over long distances.
- IoT and Massive Connectivity: With 5G, millions of devices can connect simultaneously to the network without losing performance. This will drive the adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), where LAN and WAN networks will work together to connect everything from sensors to smart devices.
5G will enable businesses to create more agile and efficient WANs, improving global connectivity while reducing reliance on traditional cable or fiber-optic connections.
- Hybrid Networks: The Future of Connectivity
The future of LAN and WAN networks is likely to be defined by the creation of hybrid networks that combine the best of both worlds. Hybrid networks can include a mix of local infrastructure (like LANs) along with access to broader networks (WANs) and will be supported by technologies like 5G, SDN, NFV, and AI.
Features of Hybrid Networks:
- Flexibility to Adapt to New Needs: Hybrid networks will allow businesses to tailor their infrastructure based on their needs, using local networks for internal activities while connecting to WANs to access cloud services or interconnect multiple locations.
- Bandwidth Optimization: With the ability to access different types of connections, hybrid networks can efficiently distribute traffic, ensuring that resources are used in the most efficient way.
- Global Connectivity with Local Efficiency: Hybrid networks can ensure that even if an organization has branches all over the world, the local user experience will remain fast and reliable thanks to optimized LANs, while WAN connectivity provides global access.
- The Role of AI in the Future of Networks
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is ushering in a new era for LAN and WAN networks. Through process automation and the ability to analyze large volumes of data, AI will enable more dynamic, intelligent, and autonomous network management.
Applications of AI in LAN and WAN Networks:
- Predictive Management: AI can analyze traffic patterns and predict demand spikes or network issues before they occur, allowing for proactive responses and minimizing downtime.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Optimization: AI can automatically adjust routes and prioritize traffic based on the real-time needs of users and applications.
- Self-Managing Networks: In the near future, LAN and WAN networks could operate autonomously, making decisions about resource allocation, device configuration, and performance optimization without human intervention.
With the advancement of these emerging technologies, LAN and WAN networks are evolving to be faster, more secure, flexible, and scalable. If you’re looking to improve your network or update your infrastructure, it’s essential to stay up-to-date on these innovations to leverage their full potential.



