Technology has become the core of our daily lives, and having an efficient home network is essential to staying connected. However, for many, setting up a network at home may seem like a daunting and technical task. But it doesn’t have to be! In this article, we’ll break the process into simple, clear, and easy-to-follow steps, perfect for beginners in the world of computer networks.
Additionally, we’ll provide practical tips to optimize your network, ensure its security, and get the most out of your internet connection. Ready to become the master of your home network? Keep reading and transform your home into a fully functional digital environment.
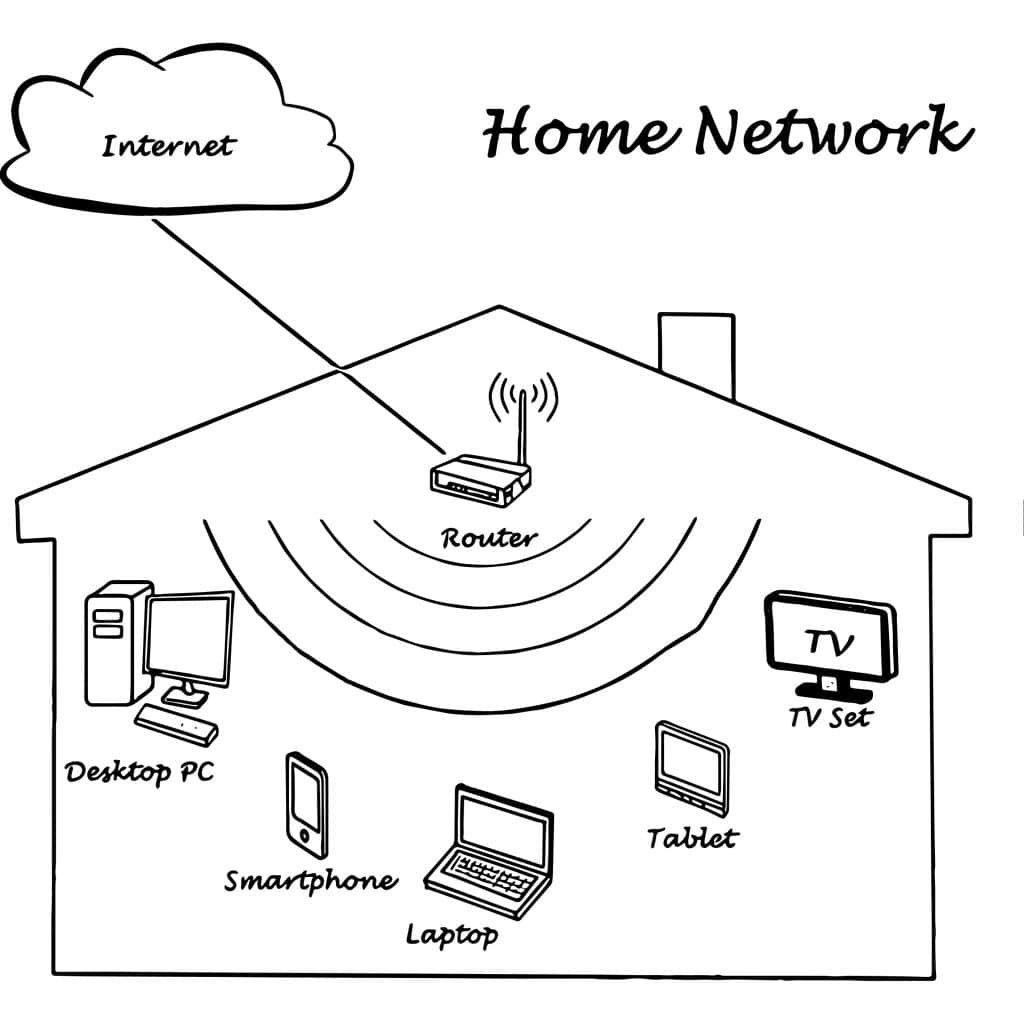
Step 1: Understand the Basic Components of a Home Network
Before diving into the setup, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the essential elements that make up a home network. These are the building blocks of any functional network:
- Internet Service Provider (ISP):
This is the provider of your internet connection. Typically, this service comes with a modem or router that serves as the starting point of your network. - The Modem:
This device connects directly to the cable or telephone line from your ISP and translates the internet signal to be usable in your home. - The Router:
While some modems include router functions, the router distributes the internet signal among various devices in your home, either wirelessly or via Ethernet cables. - End Devices:
These include smartphones, laptops, smart TVs, virtual assistants, and any other device connected to the network. - Ethernet Cables and Wi-Fi:
Ethernet cables are vital for stable and fast connections, while Wi-Fi provides the flexibility to connect devices anywhere in your home.
Why Is Understanding These Elements Important?
Knowing how these components interact will help you troubleshoot issues, make informed decisions, and customize your network to suit your needs.
Step 2: Choose the Right Location for Your Router
The placement of your router directly affects the connection quality throughout your home. If you place it in an isolated corner, some devices may experience interruptions. Follow these recommendations:
- Central Location: Place the router in the center of your home to ensure even coverage.
- Avoid Interference: Keep the router away from appliances like microwaves and cordless phones that can disrupt the Wi-Fi signal.
- Optimal Height: Install it at a high location, such as a shelf, to minimize physical obstacles and improve signal reach.
Pro Tip: If your home has multiple floors, consider using network extenders or a Wi-Fi mesh system to maximize coverage.
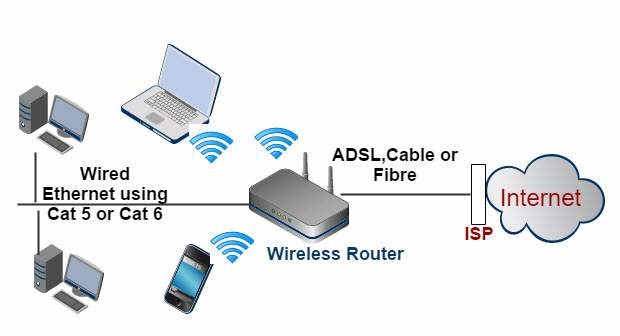
Step 3: Configure Your Router
Once you’ve found the ideal spot for your router, it’s time to set it up. Follow these steps:
- Connect the Router to the Modem:
Use an Ethernet cable to connect the router’s WAN port to your ISP modem. - Access the Router Settings:
- Connect a device to the router via Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable.
- Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Enter the login credentials provided in the router’s manual.
- Customize the Wi-Fi Network:
- Change the network name (SSID) to something easy to identify.
- Set a secure password using a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Update the Router Firmware:
Check for available software updates and apply them to ensure the best security and performance.
Security Tip: Change the default login credentials for your router to prevent unauthorized access.
Step 4: Optimize Your Network’s Speed and Performance
After setting up your network, the next step is to ensure it runs at maximum speed. Connection issues can arise from various factors, but with these tips, you can minimize problems and get the most out of your network:
- Proper Router Placement:
Ensure it’s centrally located and away from mirrors or metallic objects that reflect the signal. - Change the Wi-Fi Channel:
- Access the router settings.
- Switch the Wi-Fi channel to less congested options (e.g., channels 1, 6, and 11 for 2.4 GHz; more options are available for 5 GHz).
- Prioritize Devices (Quality of Service, QoS):
- Access the QoS settings in the router.
- Assign priority to important devices, such as your work laptop or gaming console.
- Upgrade Your Equipment:
If your network remains slow, consider upgrading to a router that supports Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E for better speed and capacity.
Key Insight: A modern router not only improves performance but also enhances security with updated encryption technologies.
Step 5: Secure Your Home Network
Security is a crucial aspect of any network. A poorly protected system can expose your devices to hackers, malware, or data theft. Here’s how to secure your network:
- Change the Wi-Fi Name and Password:
- Avoid generic names like “Home Wi-Fi.” Opt for something unique and unrelated to personal information.
- Use a long and complex password (at least 12 characters).
- Enable WPA3 or WPA2 Encryption:
- Ensure encryption is set to WPA3 (if available) or WPA2, and avoid WEP, which is outdated and vulnerable.
- Disable Remote Access:
- Unless specifically needed, disable the option to access the router remotely to reduce the risk of external intrusions.
- Set Up a Guest Network:
- Create a separate network for guests.
- Restrict this network’s access to the internet only, blocking connections to your primary devices.
- Activate the Router Firewall:
- Ensure the built-in firewall is enabled to filter malicious traffic.
Extra Tip: Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to safeguard your online activities, especially for work or sensitive operations like online banking.
Step 6: Connect and Manage Your Devices
With your home network configured and secured, it’s time to connect your everyday devices:
- Basic Device Setup:
- For mobile devices and laptops: Find your Wi-Fi network name, enter the password, and connect.
- For smart TVs and consoles: Follow the device’s setup wizard.
- Use Ethernet for Stability:
For devices requiring constant, high-speed connections (e.g., Smart TVs or PCs), use Ethernet cables. - Manage Devices via the Router Panel:
- View connected devices.
- Assign static IPs to specific devices, such as printers.
- Set Up Smart Devices:
For IoT devices, follow the instructions in their manual for proper integration.
Step 7: Troubleshoot Common Home Network Issues
Even with the best setup, problems may occasionally arise. Don’t worry—many common issues have quick and simple solutions. Here’s how to address the most frequent challenges:
1. Slow or Unstable Wi-Fi Connection
This is one of the most common issues in home networks. Try these solutions:
- Restart Your Router and Modem: Unplug them for 30 seconds, then reconnect.
- Reduce Network Congestion: Disconnect devices you’re not using and prioritize essential ones through QoS settings.
- Switch Wi-Fi Bands: If using a 2.4 GHz network, try switching to 5 GHz for faster speeds (with a shorter range).
2. Some Devices Won’t Connect
This may be due to incorrect passwords or compatibility issues:
- Verify the Password: Ensure you’re entering it correctly. Try forgetting the network on your device and reconnecting.
- Check Device Compatibility: Older devices may not support 5 GHz networks. Connect them to a 2.4 GHz network instead.
3. No Internet Connection
If your devices are connected to the network but can’t access the internet:
- Check the Modem: Ensure it’s properly connected, and verify the status indicators.
- Contact Your ISP: If everything appears fine but there’s still no internet, the issue may be with your ISP.
4. Weak Wi-Fi Signal in Certain Areas
If your signal doesn’t reach some parts of your home:
- Use Network Extenders or Powerline Adapters: Extenders amplify Wi-Fi coverage, while powerline adapters use your electrical wiring to deliver a stable connection.
- Consider a Mesh Network System: Ideal for larger homes, it ensures seamless coverage across all areas.
Step 8: Maintain and Update Your Home Network
Routine maintenance ensures your home network remains efficient and secure over time. Follow these best practices:
1. Change Your Password Regularly
Update your network password every 6–12 months, especially if you’ve shared it with guests.
2. Update Router Firmware
Manufacturers release firmware updates to improve security and performance. Check for updates manually or enable automatic updates in the router settings.
3. Monitor Network Traffic
Use the router’s admin panel to see which devices are consuming the most bandwidth. If you notice unknown devices, take immediate action by changing your password.
4. Reboot Your Router Periodically
Restarting your router monthly can help resolve performance issues and free up memory.
5. Upgrade Your Equipment When Needed
If you add more devices or need advanced features (e.g., 4K streaming or online gaming), consider upgrading to a more powerful router.
Step 9: Advanced Security and Performance Tips
As more devices connect to your network, it’s essential to enhance both security and performance. Here are advanced strategies:
Security Tips:
- Change the Router’s Default IP Address:
- Many routers use default IPs like 192.168.1.1. Changing this makes it harder for attackers to access your network.
- Example: Change it to 192.168.10.1 via the LAN settings in the router’s admin panel.
- Disable WPS and UPnP:
- WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): Though convenient, it’s vulnerable to attacks. Disable it in your router settings.
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play): This feature allows devices to auto-configure but can also be exploited by malware. Only enable it if absolutely necessary.
- Set MAC Address Filtering:
- Each device has a unique MAC address. Configure your router to only allow connections from authorized devices.
- Monitor the Network with Apps:
- Many modern routers have companion apps that let you:
- View connected devices in real-time.
- Block unknown devices.
- Manage the network remotely.
- Many modern routers have companion apps that let you:
Performance Tips:
- Separate Frequency Bands:
- If your router supports dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), assign different SSIDs to each band.
- Connect older or low-demand devices to 2.4 GHz and reserve 5 GHz for high-performance tasks like streaming or gaming.
- Set Up VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks):
- Create separate networks for different purposes, e.g., one for IoT devices and another for work devices. This boosts both security and efficiency.
- Adjust Channel Width:
- Use narrower channels (e.g., 20 MHz) in areas with high interference.
- Opt for wider channels (e.g., 40 or 80 MHz) for faster speeds in less congested areas.
- Switch to a Custom DNS Server:
- Replace your ISP’s DNS server with a faster and more private option, such as:
- Google DNS: 8.8.8.8
- Cloudflare DNS: 1.1.1.1
- Replace your ISP’s DNS server with a faster and more private option, such as:
Step 10: Integrate Smart Home Devices
Smart homes are the future, and your network should support them seamlessly. When adding devices like smart cameras, thermostats, or virtual assistants:
- Use a Dedicated Network for IoT Devices:
- Isolate IoT devices on a separate VLAN or guest network to protect your primary network from potential vulnerabilities.
- Assign Descriptive Names:
- Use clear names to identify each device, e.g., “Living Room Camera” or “Kitchen Assistant.”
- Prefer Wired Connections:
- For devices requiring constant data transmission (e.g., security cameras), use Ethernet cables for a stable connection.
Final Tips: Getting the Most from Your Home Network
Your home network should be not only functional but also efficient and secure. Follow these additional tips to optimize its performance:
- Automate Your Home:
If you use smart devices, ensure they integrate smoothly into your network without compromising security. - Set Up Parental Controls:
Protect younger users by restricting content and setting time limits through your router settings. - Use a Network-Attached Storage (NAS):
Store backups or shared files on a NAS device for easy access from any device in your network.



