In the modern business world, communication networks play a fundamental role in the success of daily operations. Whether it’s maintaining internal communication, conducting financial transactions, or interacting with clients through digital platforms, network efficiency is crucial. However, there is one aspect that often goes unnoticed, but is essential to ensuring an uninterrupted experience: Quality of Service (QoS).
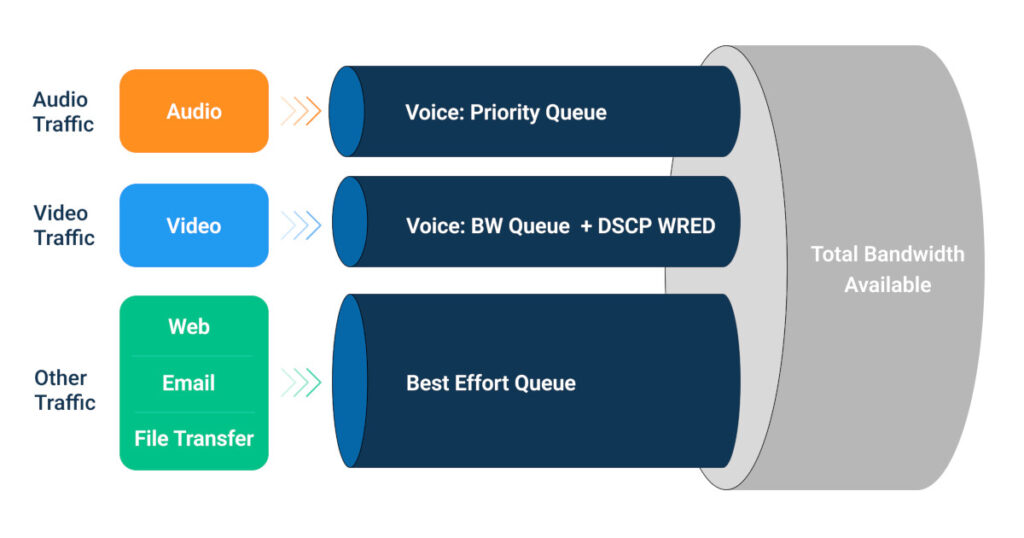
What is Quality of Service (QoS)?
Quality of Service (QoS) is a set of technologies and techniques designed to ensure optimal performance of a network by prioritizing the most important traffic and ensuring that business-critical applications are not impacted by lower-priority traffic. In simple terms, QoS manages bandwidth, latency, and packet loss to ensure that essential services and applications run efficiently and without interruption.
In a business network, the proper implementation of QoS can be the difference between a smooth user experience and a congested network full of delays, outages, and service drops. In this article, we will explore the importance of QoS in business networks, its benefits, best practices for implementation, and how it can optimize productivity, efficiency, and customer experience.
The Need for QoS in a Modern Business Environment
In today’s businesses, connectivity is more than just a convenience; it is a critical necessity. Digital transformation has changed the way businesses operate, and a robust, reliable network infrastructure is now the heart of innovation. Work teams depend on constant connectivity to access cloud-based applications, hold video conferences, send data to remote servers, and more.
However, network traffic congestion is a growing problem. Business systems are faced with a massive volume of data circulating through the network, and often, low-priority applications like web browsing or email compete for the same bandwidth as critical applications. Without proper traffic management, network resources can become congested, leading to poor user experiences and decreased productivity.
This is particularly problematic when networks are used to run real-time business applications, such as video conferences, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, accounting software, and other key applications. When latency and packet loss affect these services, employees can experience interruptions that slow down daily operations and impact decision-making.
Implementing a QoS strategy not only helps avoid these issues but also optimizes network performance and ensures that critical applications always have access to the necessary resources. In fact, a well-implemented QoS network can more efficiently handle a large number of connected devices, which is crucial as businesses adopt Internet of Things (IoT) and other emerging technologies.
The Benefits of Quality of Service in Business Networks
Implementing QoS in a company’s networks can generate tangible benefits that positively impact efficiency and productivity. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Prioritization of Critical Traffic
One of the most immediate benefits of QoS is the ability to prioritize data traffic based on its importance. Critical applications such as video conferences, data transfers, and collaboration apps receive higher priority compared to less urgent traffic like web browsing or large file transfers. This ensures that key communications are not affected by network congestion. - Reduction in Latency
Latency is the delay that data experiences while traveling through the network. In business applications, especially those requiring real-time interaction, such as video calls or CRM applications, high latency can be detrimental. QoS helps reduce this delay by optimizing data routing and ensuring high-priority packets are transmitted more efficiently. - Increased Reliability and Service Continuity
Reliability is a crucial factor for business networks. A network failure or service interruption can paralyze business operations, leading to revenue and reputation loss. QoS helps minimize these risks by ensuring that the most important traffic is properly managed, even during times of high congestion. - Optimization of Network Resources
A network’s capacity is not infinite, and businesses must optimize resource usage to ensure that the network infrastructure is working as efficiently as possible. By dynamically managing traffic, QoS ensures that resources are allocated appropriately, reducing bandwidth wastage and maximizing network capacity. - Improved End-User Experience
An efficient business network directly improves the experience of employees and clients. Low latency, higher reliability, and proper application prioritization ensure that users can perform their tasks without interruptions, improving overall satisfaction and productivity.
The Challenges of Implementing QoS in Business Networks
Although the benefits of QoS are undeniable, effectively implementing this technology can present certain challenges. Some common obstacles businesses face when trying to implement QoS include:
- Complexity in Configuration
Properly configuring QoS can be a technical and complex process. Network administrators must identify traffic types, classify applications, and set prioritization rules, all while ensuring that there is no negative impact on the overall network performance. - Implementation Costs
Implementing QoS often requires upgrading network equipment, such as routers, switches, and firewalls, which can incur additional costs. For smaller businesses, this may be a significant barrier, although the long-term benefits may justify the investment. - Ongoing Management and Maintenance
QoS is not a one-time solution but requires continuous monitoring to ensure the QoS policies remain effective as business needs and network traffic evolve. This requires resources and a trained IT team to manage and adjust configurations.
How to Implement QoS in Business Networks
Implementing QoS in a business network is not a simple task, but the benefits it provides make the effort worthwhile. Here are some key steps for effectively implementing QoS:
- Assess the Company’s Needs
The first step in implementing QoS is understanding the specific needs of the business. What applications are critical to the business? Which ones are most sensitive to latency? Which traffic should take priority in daily operations?
Once the most important applications and services for the business are understood, a traffic profile should be created to identify how each type of traffic should be handled. This may include, for example, prioritizing video conferences, financial transactions, and business management applications, while reducing the priority of emails or web browsing.
- Network Traffic Classification
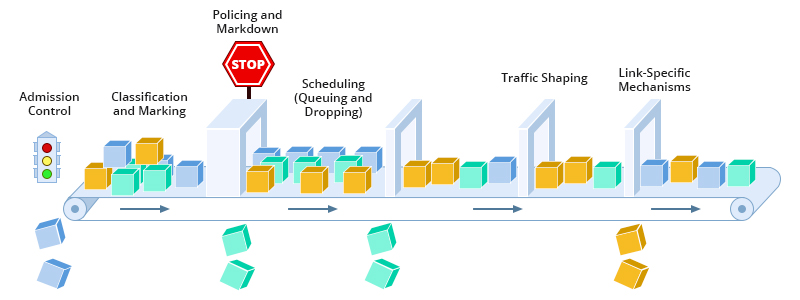
After identifying the priority services and applications, the next step is to classify network traffic. Packet classification involves tagging traffic based on its importance. There are different ways to classify packets, such as by IP address, protocol, port, or service type. This classification is crucial for network devices to effectively apply QoS policies. - Assigning Priorities and Resources
Once traffic is classified, priorities must be assigned to each type of traffic. Various prioritization strategies exist, such as using priority queues or congestion control, to ensure that critical traffic receives the necessary resources. For example, in a network with QoS, voice or video traffic may have higher priority than large file downloads. - Implementing QoS Policies
QoS policies define how network resources should be managed and how priorities are assigned. These policies are implemented at the network device level, such as routers and switches, to ensure that rules are applied throughout the infrastructure.
Policies can include different types of management techniques, such as:
- Traffic shaping: Limits data traffic to ensure that critical applications are not affected by excess non-essential traffic.
- Queue policy: Organizes data packets into different queues based on their priority, ensuring that higher-priority packets are transmitted first.
- Congestion control: Monitors the network to ensure that traffic stays within optimal performance limits.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustments
Once QoS has been implemented, the work doesn’t end there. Continuous monitoring is necessary to ensure that QoS policies remain effective. As network traffic changes and business needs evolve, QoS policies must be adjusted to maintain optimal performance.
Monitoring should include evaluating bandwidth utilization, latency, and packet loss. Network administrators must be vigilant for any signs that performance is declining or that QoS policies are not working as expected. Traffic analysis can also help identify areas for improvement and adjust QoS policies to maximize network efficiency.
Best Practices for Implementing QoS
To ensure that QoS implementation is successful, it’s important to follow some best practices. These recommendations will help businesses make the most of the technology and avoid common mistakes during the implementation process:
- Detailed Planning
Before implementing QoS, detailed planning must be carried out. This includes identifying critical applications, classifying traffic, and defining prioritization policies. Proper planning ensures that desired results are achieved and that the network functions smoothly from the outset. - Involve the Entire IT Team
Implementing QoS should not be the responsibility of just one person or team. It is important that the entire IT team is involved in the process, from planning to implementation and continuous monitoring. This ensures that all areas of the network are covered and that potential issues can be addressed quickly. - Set Clear QoS Objectives
It is crucial to set clear QoS objectives, such as latency expectations, application prioritization, and required bandwidth for certain services. Having these objectives well defined allows network administrators to adjust policies effectively to meet business requirements. - Evaluate Current Network Infrastructure
Before implementing QoS, businesses should evaluate their current network infrastructure to identify potential bottlenecks or hardware limitations that could affect QoS performance. Older networks or outdated network devices may not be capable of handling QoS effectively, and infrastructure updates or changes may be necessary. - Perform Testing and Validation
Before putting QoS configurations into production, thorough testing should be conducted. This includes simulating different types of traffic to ensure that QoS policies work correctly and that critical applications receive sufficient bandwidth and priority.
The Future of QoS in Business Networks
As business networks continue to evolve, so does the concept of Quality of Service. The increasing demand for cloud-based services, the Internet of Things (IoT), and high-performance applications are driving the need for more advanced QoS management. Additionally, the rise of network virtualization and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) enables more flexible and dynamic QoS management.
The future of QoS in business networks will focus on the intelligent automation of traffic policies, using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to optimize performance in real-time. These technologies will allow businesses to adapt to changing network conditions and ensure optimal performance under all circumstances.
How QoS Impacts the End-User Experience
The end-user experience is one of the most important factors influenced by Quality of Service (QoS) in business networks. In today’s environment, where remote work and digital interactions are becoming increasingly common, network connection quality has a direct impact on employee and customer productivity, satisfaction, and efficiency. Effectively implementing QoS ensures that business services are delivered reliably, without interruptions, and with the least possible latency.
- Improvement in Real-Time Communications
Video calls and real-time communication applications are critical in any modern business. Whether for internal meetings, customer calls, or remote collaboration, these tools require low latency and constant bandwidth to ensure a smooth experience. Without QoS, video or voice traffic may be impacted by network congestion, leading to drops, screen freezes, and audio distortion.
With QoS, voice and video traffic can be prioritized to ensure that employee video calls and communication with customers run smoothly. This not only improves internal productivity but also helps maintain a professional image with clients, who expect clear communication without interruptions.
- Optimizing the Customer Experience
Customer-facing applications such as customer support systems, self-service portals, and sales platforms depend on network speed and reliability to deliver a satisfying experience. If a business lacks an adequate QoS system, customers may face long wait times, slow-loading web pages, or inefficient applications.
Implementing QoS allows prioritizing traffic for customer support or e-commerce systems, ensuring that customers can interact with platforms without issues, even during peak demand. This reduces user frustration and improves customer loyalty by providing them with a faster, more reliable experience.
- Increase in Internal Productivity
Within businesses, employees use multiple applications and tools, from productivity software and cloud storage to collaboration tools. When these applications run without proper prioritization, there is a risk that the most important ones may be overshadowed by lower-priority traffic, such as large file downloads or software updates.
By implementing QoS, applications essential to daily operations receive higher priority, ensuring that employees can work uninterrupted, accessing critical resources quickly. This directly translates into higher efficiency and productivity in everyday tasks.
The Relationship Between QoS and Network Security
One aspect that is often overlooked is the relationship between Quality of Service and network security. While QoS focuses on the efficiency of data traffic, it can also play a crucial role in protecting the business network. By optimizing traffic flow, QoS mechanisms can also contribute to enhancing the security of the network infrastructure.
- Preventing Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks are becoming more common, and one of the objectives of these attacks is to overload the network with unwanted traffic, making business applications and online services unavailable to legitimate users. While QoS is not specifically designed to block these attacks, it can help mitigate their impact.
By allocating more bandwidth and prioritizing legitimate traffic, DDoS attacks can be managed more effectively. Rather than allowing malicious traffic to consume all bandwidth, QoS mechanisms ensure that essential services continue functioning properly.
- Network Segmentation and Security Traffic Prioritization
Network segmentation is a technique that helps reduce exposure to threats by dividing the network into smaller segments, each with specific security policies. QoS can be used to prioritize security traffic, such as firewall updates, security audits, and encrypted communications, ensuring that these services always have the necessary resources to run without interruptions.
Additionally, by prioritizing security-related traffic, businesses can detect potential vulnerabilities more quickly and respond to threats more effectively.
Investing in QoS as a Key Factor for Business Success
Quality of Service (QoS) in business networks is not just a technical matter; it is a fundamental strategy to ensure efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. As businesses increasingly rely on their networks to operate and deliver their products and services, implementing QoS becomes a key investment for long-term success.
It’s not just about managing traffic efficiently, but about creating a network infrastructure that is agile, secure, and capable of adapting to changing demands. From improving the end-user experience to optimizing internal communications and protecting the network, the benefits of QoS are numerous.
For businesses looking to maintain their competitiveness in an increasingly digital world, ensuring an efficient and reliable network is an indispensable requirement. Effectively implementing QoS not only helps avoid congestion and latency issues but also improves network resilience to potential threats, optimizes resource usage, and, most importantly, enhances the overall experience for both employees and customers.
Ultimately, Quality of Service is a key differentiator for businesses seeking to offer tangible value to their clients and improve their internal operations. Now is the time to take the step toward a smarter and more efficient business network, using QoS as the tool to achieve it.



